tKl_i2c | I2C Driver
Brief Description
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) is a serial synchronous communication bus. The I2C serial bus has two signal lines: a bidirectional data line SDA and a clock line SCL. All serial data SDA connected to I2C bus devices are connected to the SDA of the bus, and each device's clock line SCL is connected to the SCL of the bus.
The typical wiring method for I2C is as follows:
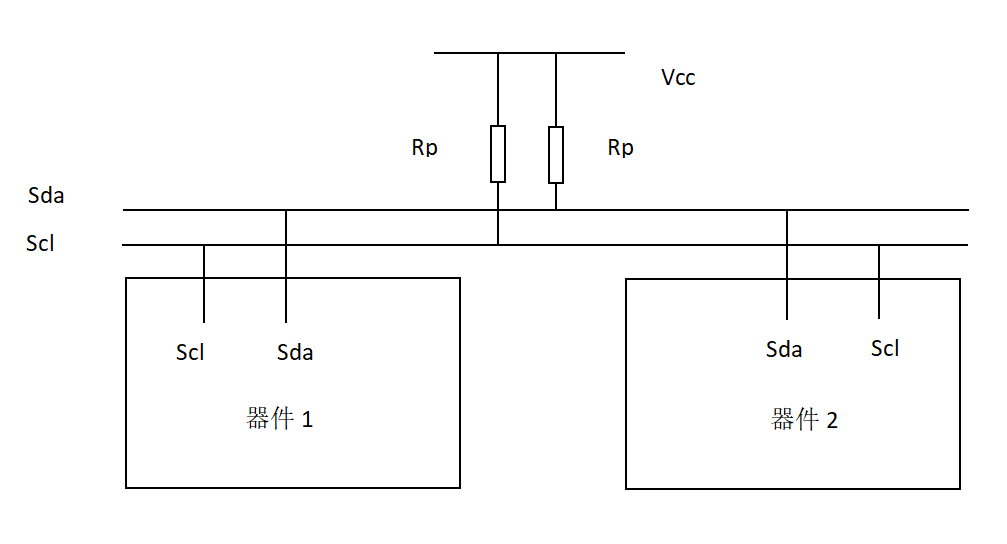
Communication on the bus is controlled by the master, which means the master is the device that transmits data (issues start signals), generates clock signals, and issues stop signals at the end of the transmission. The device being accessed by the master is called the slave. Each device connected to the I2C bus has a unique address for the master to access. Data transmission between the master and the slave can be from the master to the slave or from the slave to the master. I2C supports 7-bit or 10-bit slave device address modes. After the start condition, the first byte on the I2C bus determines which controller will be selected by the master. When the master outputs an address, each slave device in the system compares the address after the start condition with its own address. If they are the same, the slave recognizes that it has been addressed by the master.
API Description
tkl_i2c_init
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_init(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port, const TUYA_IIC_BASE_CFG_T *cfg);
-
Function Description:
- Initialize the corresponding I2C instance through the port number and base configuration, and return the initialization result.
-
Parameters:
-
port: Port number. -
cfg: I2C base configuration, including role, speed, and address width.typedef struct { TUYA_IIC_ROLE_E role; TUYA_IIC_SPEED_E speed; TUYA_IIC_ADDR_MODE_E addr_width; } TUYA_IIC_BASE_CFG_T;TUYA_IIC_ROLE_E:
Name Definition Remarks TUYA_IIC_MODE_MASTER I2C Master Mode TUYA_IIC_MODE_SLAVE I2C Slave Mode TUYA_IIC_SPEED_E:
Name Definition Remarks TUYA_IIC_BUS_SPEED_100K I2C Standard Speed (100KHz) TUYA_IIC_BUS_SPEED_400K I2C Fast Speed (400KHz) TUYA_IIC_BUS_SPEED_1M I2C Standard+ Speed (1MHz) TUYA_IIC_BUS_SPEED_3_4M I2C High Speed (3.4MHz) TUYA_IIC_ADDR_MODE_E:
Name Definition Remarks TUYA_IIC_ADDRESS_7BIT 7-bit Address Mode TUYA_IIC_ADDRESS_10BIT 10-bit Address Mode
-
-
Return Value:
- OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
tkl_i2c_deinit
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_deinit(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port)
- Function Description:
- De-initialize the I2C instance. This interface will stop the I2C and release related software and hardware resources.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
tkl_i2c_irq_init
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_irq_init(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port, TUYA_I2C_IRQ_CB cb);
-
Function Description:
- Initialize I2C interrupts.
-
Parameters:
-
port: Port number. -
cb: I2C interrupt callback function.The callback function type TUYA_I2C_IRQ_CB is defined as follows:
typedef void (*TUYA_I2C_IRQ_CB)(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port, TUYA_I2C_IRQ_EVT_E event);Where
portis the port number, andeventis the event type passed to the callback function.The I2C callback event enumeration type TUYA_I2C_IRQ_EVT_E is defined as follows:
Name Definition Remarks TUYA_IIC_EVENT_TRANSFER_DONE Transfer Complete Event TUYA_IIC_EVENT_TRANSFER_INCOMPLETE Transfer Incomplete Event TUYA_IIC_EVENT_SLAVE_TRANSMIT Slave Transmit Operation Request Event TUYA_IIC_EVENT_SLAVE_RECEIVE Slave Receive Operation Request Event TUYA_IIC_EVENT_ADDRESS_NACK Address Not Acknowledged Event TUYA_IIC_EVENT_GENERAL_CALL Indicates Received General Call (Address is 0) Event TUYA_IIC_EVENT_ARBITRATION_LOST Master Arbitration Lost Event TUYA_IIC_EVENT_BUS_ERROR Bus Error Event TUYA_IIC_EVENT_BUS_CLEAR Bus Clear Complete Event
-
-
Return Value:
- OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
tkl_i2c_irq_enable
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_irq_enable(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port);
- Function Description:
- Enable I2C interrupts.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
tkl_i2c_irq_disable
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_irq_disable(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port);
- Function Description:
- Disable I2C interrupts.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
tkl_i2c_master_send
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_master_send(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port, uint16_t dev_addr, const void *data, uint32_t size, BOOL_T xfer_pending);
- Function Description:
- Start data transmission when I2C is in master mode.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.dev_addr: Slave device address.data: Buffer address of data to be sent.size: Length of data to be sent.xfer_pending: Whether to send a stop bit after sending. 1 - Do not send stop bit, 0 - Send stop bit.
- Return Value:
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
tkl_i2c_master_receive
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_master_receive(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port, uint16_t dev_addr, void *data, uint32_t size, BOOL_T xfer_pending);
- Function Description:
- Start data reception when I2C is in master mode.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.dev_addr: Slave device address.data: Buffer address for received data.size: Length of data to be received.xfer_pending: Whether to send a stop bit after receiving. 1 - Do not send stop bit, 0 - Send stop bit.
- Return Value:
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
tkl_i2c_set_slave_addr
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_set_slave_addr(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port, uint16_t dev_addr);
- Function Description:
- Configure the I2C slave device address.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.dev_addr: I2C slave device communication address.
- Return Value:
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
tkl_i2c_slave_send
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_slave_send(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port, const void *data, uint32_t size);
- Function Description:
- Start data transmission when I2C is in slave mode.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.data: Buffer address of data to be sent.size: Length of data to be sent by the slave.
- Return Value:
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
tkl_i2c_slave_receive
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_slave_receive(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port, void *data, uint32_t size);
- Function Description:
- Start data reception when I2C is in slave mode.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.data: Buffer address for received data.size: Length of data to be received.
- Return Value:
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
tkl_i2c_get_status
TUYA_IIC_STATUS_T tkl_i2c_get_status(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port);
- Function Description:
- Get the current status of I2C.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- I2C status structure. I2C status definitions are in TUYA_I2C_STATUS_T.
tkl_i2c_get_data_count
int32_t tkl_i2c_get_data_count(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port);
- Function Description:
- Get the number of data transmitted by I2C.
- For tkl_i2c_master_send, the number of bytes transmitted or sent.
- For tkl_i2c_master_receive, the number of bytes received.
- For tkl_i2c_slave_send, the number of bytes transmitted.
- For tkl_i2c_slave_receive, the number of bytes received.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- Number of transmitted data.
TUYA_IIC_STATUS_T:
| Name | Definition | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| busy : 1 | Transmission or Sending Busy Status | |
| mode : 1 | Mode Bit. 1 - Master, 0 - Slave | |
| direction : 1 | Transmission Direction: 1 - Receive, 0 - Send | |
| general_call : 1 | General Call Indicator | |
| arbitration_lost : 1 | Master Lost Arbitration | |
| bus_error : 1 | Bus Error |
tkl_i2c_reset
OPERATE_RET tkl_i2c_reset(TUYA_I2C_NUM_E port);
- Function Description:
- Reset I2C.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
OS_ADAPTER_I2Csection in the filetuya_error_code.h.
- Error code, OPRT_OK for success, others please refer to the
Examples
Example 1: I2C Master Example
static uint16_t cb_transfer_flag = 0xff;
static void i2c_event_cb_fun(int32_t idx, TUYA_IIC_IRQ_EVT_E event)
{
if (idx == I2C_NUM_0){
cb_transfer_flag = event;
}
}
void tuya_i2c_master_test(void)
{
OPERATE_RET ret;
TUYA_IIC_BASE_CFG_T cfg;
//receive buffer
char rcv_buf[10];
//data to send
char send_buf[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_0, TUYA_IIC0_SCL);
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_1, TUYA_IIC0_SDA);
cfg.role = TUYA_IIC_MODE_MASTER;
cfg.speed = TUYA_IIC_BUS_SPEED_100K;
cfg.addr_width = TUYA_IIC_ADDRESS_7BIT;
ret = tkl_i2c_init(I2C_NUM_0, &cfg);
if (ret != OPRT_OK) {
//fail
return;
}
ret = tkl_i2c_irq_init(I2C_NUM_0, i2c_event_cb_fun);
if (ret != OPRT_OK) {
//fail
return;
}
ret = tkl_i2c_irq_enable(I2C_NUM_0);
if (ret != OPRT_OK) {
//fail
return;
}
ret = tkl_i2c_master_send(I2C_NUM_0, 0x57, send_buf, sizeof(send_buf), 0);
if (ret < 0) {
//failed
}
while (cb_transfer_flag == 0xff);
//check transfer result
if (cb_transfer_flag == IIC_EVENT_TRANSFER_DONE) {
//transmit done
} else {
//failed
}
cb_transfer_flag = 0xff;
ret = tkl_i2c_master_receive(I2C_NUM_0, 0x57, rcv_buf, sizeof(rcv_buf), 0);
if (ret < 0) {
//failed
}
while (cb_transfer_flag == 0xff);
//check transfer result
if (cb_transfer_flag == IIC_EVENT_TRANSFER_DONE) {
//transmit done
} else {
//failed
}
ret = tkl_i2c_irq_disable(I2C_NUM_0);
if (ret != OPRT_OK) {
//fail
return;
}
//uninitialize iic
ret = tkl_i2c_deinit(I2C_NUM_0);
if (ret != 0) {
//failed
}
}
Example 2: I2C Slave Example
void tuya_i2c_slave_test(void)
{
OPERATE_RET ret;
TUYA_IIC_BASE_CFG_T cfg;
TUYA_IIC_STATUS_T st;
//receive buffer
char rcv_buf[10];
//data to send
char send_buf[10] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
int32_t cnt = 100;
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_0, TUYA_IIC0_SCL);
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_1, TUYA_IIC0_SDA);
cfg.role = TUYA_IIC_MODE_SLAVE;
cfg.speed = TUYA_IIC_BUS_SPEED_100K;
cfg.addr_width = TUYA_IIC_ADDRESS_7BIT;
ret = tkl_i2c_init(I2C_NUM_0, &cfg);
if (ret != OPRT_OK) {
//fail
return;
}
ret = tkl_i2c_set_slave_addr(I2C_NUM_0, 0x57);
if (ret != OPRT_OK) {
//fail
return;
}
ret = tkl_i2c_slave_send(I2C_NUM_0, send_buf, sizeof(send_buf));
if (ret < 0) {
//failed
}
//wait send done, waiting for 100 ms max
st.busy = 1;
cnt = 100;
while(cnt--) {
tkl_system_sleep(1);
//check status
st = tkl_i2c_get_status(I2C_NUM_0);
//transmit done
if (st.busy == 0){
break;
}
}
ret = tkl_i2c_slave_receive(I2C_NUM_0, rcv_buf, sizeof(rcv_buf));
if (ret < 0) {
//failed
}
//wait send done, waiting for 100 ms max
st.busy = 1;
cnt = 100;
while(cnt--) {
tkl_system_sleep(1);
//check status
st = tkl_i2c_get_status(I2C_NUM_0);
//transmit done
if (st.busy == 0){
break;
}
}
//uninitialize iic
ret = tkl_i2c_deinit(I2C_NUM_0);
if (ret != 0) {
//failed
}
}