tkl_spi | SPI Driver
Brief Description
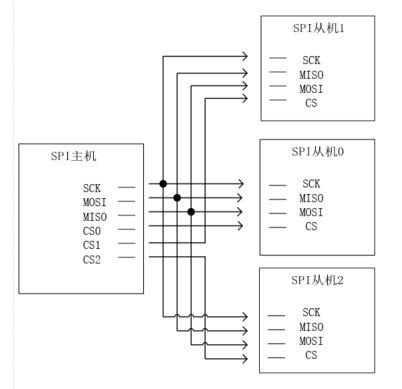
SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) is a high-speed, full-duplex, synchronous communication bus. SPI operates in a master-slave mode, typically with one master device and one or more slave devices.
The signal lines of the SPI controller are described as follows:
- MISO: Master device data input, slave device data output;
- MOSI: Master device data output, slave device data input;
- SCK: Clock signal, generated by the master device;
- CS: Slave device enable signal, controlled by the master device. This signal can be part of the SPI peripheral or implemented with a GPIO pin.
The typical wiring method for the SPI bus is as follows:
The SPI bus supports four working modes, depending on the combination of the serial synchronous clock polarity (CPOL) and the serial synchronous clock phase (CPHA).
CPOL is used to determine the idle level of the SCLK clock signal. When CPOL=0, the idle level is low, and when CPOL=1, the idle level is high. CPHA is used to determine the sampling time. When CPHA=0, data is sampled on the first clock edge of each cycle and output on the second clock edge. When CPHA=1, data is sampled on the second clock edge of each cycle and output on the first clock edge. The clock phase and polarity of the SPI master module and the communicating peripheral should be consistent.
The timing diagrams for the four working modes are described as follows:
- Mode 0: CPOL=0, CPHA=0. The SCK serial clock line is idle at a low level, and data is sampled on the rising edge of the SCK clock and switched on the falling edge.
- Mode 1: CPOL=0, CPHA=1. The SCK serial clock line is idle at a low level, and data is sampled on the falling edge of the SCK clock and switched on the rising edge.
- Mode 2: CPOL=1, CPHA=0. The SCK serial clock line is idle at a high level, and data is sampled on the falling edge of the SCK clock and switched on the rising edge.
- Mode 3: CPOL=1, CPHA=1. The SCK serial clock line is idle at a high level, and data is sampled on the rising edge of the SCK clock and switched on the falling edge.
API Description
tkl_spi_init
OPERATE_RET tkl_spi_init(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port, const TUYA_SPI_BASE_CFG_T *cfg);
-
Function Description:
- Initializes the corresponding SPI instance via the port number and basic configuration, returning the initialization result.
-
Parameters:
-
port: Port number. -
cfg: SPI basic configuration.typedef struct { TUYA_SPI_ROLE_E role; TUYA_SPI_MODE_E mode; TUYA_SPI_TYPE_E type; TUYA_SPI_DATABITS_E databits; TUYA_SPI_BIT_ORDER_E bitorder; uint32_t freq_hz; uint32_t spi_dma_flags; /*!< SPI dma format , 1 use dma */ } TUYA_SPI_BASE_CFG_T;TUYA_SPI_ROLE_E:
Name Definition Remarks TUYA_SPI_ROLE_INACTIVE SPI inactive TUYA_SPI_ROLE_MASTER SPI full-duplex master mode TUYA_SPI_ROLE_SLAVE SPI full-duplex slave mode TUYA_SPI_ROLE_MASTER_SIMPLEX SPI half-duplex master mode TUYA_SPI_ROLE_SLAVE_SIMPLEX SPI half-duplex slave mode TUYA_SPI_MODE_E:
Name Definition Remarks TUYA_SPI_MODE0 CPOL = 0, CPHA = 0 TUYA_SPI_MODE1 CPOL = 0, CPHA = 1 TUYA_SPI_MODE2 CPOL = 1, CPHA = 0 TUYA_SPI_MODE3 CPOL = 1, CPHA = 1 TUYA_SPI_TYPE_E:
Name Definition Remarks TUYA_SPI_AUTO_TYPE SS pin mode, hardware auto-config SS: slave select, corresponds to CS pin TUYA_SPI_SOFT_TYPE SS pin mode, software manual-config TUYA_SPI_SOFT_ONE_WIRE_TYPE Three-wire mode, SS pin invalid TUYA_SPI_DATABITS_E:
Name Definition Remarks TUYA_SPI_DATA_BIT8 8-bit data mode TUYA_SPI_DATA_BIT16 16-bit data mode TUYA_SPI_BIT_ORDER_E:
Name Definition Remarks TUYA_SPI_ORDER_MSB2LSB High bit (MSB) first, low bit (LSB) last TUYA_SPI_ORDER_LSB2MSB Low bit (LSB) first, high bit (MSB) last
-
-
Return Value:
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tuya_error_code.h, OS_ADAPTER_SPI definition section.
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tkl_spi_deinit
OPERATE_RET tkl_spi_deinit(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port);
- Function Description:
- Deinitializes the SPI instance. This interface will stop the SPI instance and release related software and hardware resources.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tuya_error_code.h, OS_ADAPTER_SPI definition section.
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tkl_spi_send
OPERATE_RET tkl_spi_send(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port, void *data, uint16_t size);
- Function Description:
- SPI starts data transmission.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.data: Buffer address of data to be sent.size: Length of data to be sent.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tuya_error_code.h, OS_ADAPTER_SPI definition section.
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tkl_spi_recv
OPERATE_RET tkl_spi_recv(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port, void *data, uint16_t size);
- Function Description:
- SPI starts data reception.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.data: Buffer address of data to be received.size: Length of data to be received.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tuya_error_code.h, OS_ADAPTER_SPI definition section.
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tkl_spi_transfer
OPERATE_RET tkl_spi_transfer(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port, void* send_buf, void* receive_buf, uint32_t length);
- Function Description:
- SPI starts data transfer.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.send_buf: Buffer address of data to be sent.receive_buf: Buffer address of data to be received.length: Length.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tuya_error_code.h, OS_ADAPTER_SPI definition section.
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tkl_spi_abort_transfer
OPERATE_RET tkl_spi_abort_transfer(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port);
- Function Description:
- SPI aborts data transfer or aborts data sending (receiving).
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tuya_error_code.h, OS_ADAPTER_SPI definition section.
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tkl_spi_get_status
OPERATE_RET tkl_spi_get_status(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port, TUYA_SPI_STATUS_T *status);
- Function Description:
- Gets the SPI status at the current time.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- The structure of the SPI status, the definition of the SPI status can be found in the definition of
TUYA_SPI_STATUS_T.
- The structure of the SPI status, the definition of the SPI status can be found in the definition of
TUYA_SPI_STATUS_T:
| Name | Definition | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| busy : 1 | Transmission/reception busy status | 1 is valid |
| data_lost : 1 | Data lost | 1 is valid |
| mode_fault : 1 | Mode error | 1 is valid |
tkl_spi_irq_init
OPERATE_RET tkl_spi_irq_init(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port, TUYA_SPI_IRQ_CB cb);
- Function Description:
- SPI interrupt initialization.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.cb: Interrupt callback function.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tuya_error_code.h, OS_ADAPTER_SPI definition section.
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tkl_spi_irq_enable
OPERATE_RET tkl_spi_irq_enable(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port);
- Function Description:
- Enables SPI interrupt.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tuya_error_code.h, OS_ADAPTER_SPI definition section.
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tkl_spi_irq_disable
OPERATE_RET tkl_spi_irq_disable(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port);
- Function Description:
- Disables SPI interrupt.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tuya_error_code.h, OS_ADAPTER_SPI definition section.
- OPRT_OK Success, others please refer to the file
tkl_spi_get_data_count
int32_t tkl_spi_get_data_count(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port);
- Function Description:
- Gets the SPI transmission byte length.
- Parameters:
port: Port number.
- Return Value:
- Returns < 0 on error. Returns >= 0 for the byte length of the last transmission. This can be from any of the operations
tkl_spi_send,tkl_spi_recv, ortkl_spi_transfer.
- Returns < 0 on error. Returns >= 0 for the byte length of the last transmission. This can be from any of the operations
Examples
1. SPI Example 1
void tuya_spi_test1(void)
{
OPERATE_RET ret;
TUYA_SPI_BASE_CFG_T cfg;
TUYA_SPI_STATUS_T status;
//receive buffer
char rcv_buf[8];
//data to send
char send_buf[8] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_0, TUYA_SPI0_MISO);
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_1, TUYA_SPI0_MOSI);
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_2, TUYA_SPI0_CS);
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_3, TUYA_SPI0_CLK);
cfg.role = TUYA_SPI_ROLE_MASTER;
cfg.mode = TUYA_SPI_MODE0;
cfg.type = TUYA_SPI_AUTO_TYPE;
cfg.databits = TUYA_SPI_DATA_BIT8;
cfg.bitorder = TUYA_SPI_ORDER_MSB2LSB;
cfg.freq_hz = 1000000;
ret = tkl_spi_init(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, &cfg);
if (ret != OPRT_OK) {
//fail
return;
}
ret = tkl_spi_send(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, send_buf, 8);
if (ret < 0) {
//failed
}
tkl_spi_get_status(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, &status);
while (status.busy) {
tkl_spi_get_status(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, &status);
tkl_system_sleep(2);
}
ret = tkl_spi_recv(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, rcv_buf, 8);
if (ret < 0) {
//failed
}
tkl_spi_get_status(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, &status);
while (status.busy) {
tkl_spi_get_status(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, &status);
tkl_system_sleep(2);
}
ret = tkl_spi_transfer(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, send_buf, rcv_buf, 6);
if (ret < 0) {
//failed
}
tkl_spi_get_status(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, &status);
while (status.busy) {
tkl_spi_get_status(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, &status);
tkl_system_sleep(2);
}
//uninitialize iic
ret = tkl_spi_deinit(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0);
if (ret != 0) {
//failed
}
}
2. SPI Using Interrupt Example 2
int event_flag = -1;
static void spi_event_cb(TUYA_SPI_NUM_E port, TUYA_SPI_IRQ_EVT_E event)
{
//printf("\nspi_event_cb_fun:%d\n",event);
event_flag = event;
}
void tuya_spi_test2(void)
{
OPERATE_RET ret;
TUYA_SPI_BASE_CFG_T cfg;
TUYA_SPI_STATUS_T status;
//receive buffer
char rcv_buf[6];
//data to send
char send_buf[6] = {0x90,0x0,0x0,0x0,0x0,0x0};
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_0, TUYA_SPI0_MISO);
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_1, TUYA_SPI0_MOSI);
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_2, TUYA_SPI0_CS);
tkl_io_pinmux_config(TUYA_IO_PIN_3, TUYA_SPI0_CLK);
cfg.role = TUYA_SPI_ROLE_MASTER;
cfg.mode = TUYA_SPI_MODE0;
cfg.type = TUYA_SPI_AUTO_TYPE;
cfg.databits = TUYA_SPI_DATA_BIT8;
cfg.bitorder = TUYA_SPI_ORDER_MSB2LSB;
cfg.freq_hz = 1000000;
ret = tkl_spi_init(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, &cfg);
if (ret != OPRT_OK) {
//fail
return;
}
tkl_spi_irq_init(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0 , spi_event_cb);
tkl_spi_irq_enable(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0);
event_flag = -1;
ret = tkl_spi_transfer(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, send_buf, rcv_buf, 6);
if (ret < 0) {
//failed
}
while (TUYA_SPI_EVENT_TRANSFER_COMPLETE != event_flag) {
tkl_system_sleep(2);
}
//up Transfer Complete
event_flag = -1;
ret = tkl_spi_send(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, send_buf, 6);
if (ret < 0) {
//failed
}
while (TUYA_SPI_EVENT_TX_COMPLETE != event_flag) {
tkl_system_sleep(2);
}
// up send Complete,
event_flag = -1;
ret = tkl_spi_recv(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0, rcv_buf, 6);
if (ret < 0) {
//failed
}
while (TUYA_SPI_EVENT_RX_COMPLETE != event_flag) {
tkl_system_sleep(2);
}
// up recv Complete,
tkl_spi_irq_disable(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0);
//uninitialize iic
ret = tkl_spi_deinit(TUYA_SPI_NUM_0);
if (ret != 0) {
//failed
}
}